AI-generated media, including deepfakes, is revolutionizing digital content production, offering new possibilities and challenges.A recent study in United States revealed that 74% of consumers have doubted the authenticity of photos or videos, even from reputable news sources, while 93% want to know how content is created or edited.
Aware of the growing concerns over content authenticity and transparency, social media platforms and advertising platforms have taken the lead by adopting C2PA (Coalition for Content Provenance and Authenticity) standards, which are designed to embed and verify provenance and authenticity metadata in digital assets.
These efforts aim to provide clear, verifiable information about digital content creation while setting new benchmarks for transparency and accountability.
This feature examines the implementation of C2PA across social media and advertising platforms, exploring how they are progressing in adopting these standards.
TikTok
In 2022, TikTok developed a synthetic media policy to address concerns like misinformation, harassment, and risks from undisclosed AI-generated content (AIGC). The policy balances mitigating harm with fostering creative expression. By April 2023, TikTok required creators to disclose synthetic media using labels or captions and introduced a toggle feature for consistent labeling. Expert collaboration helped design the system to ensure effective disclosure without causing user fatigue.
TikTok’s policies, aligned with the PAI Framework, prioritize transparency and harm prevention through AI Effect labels, a creator toggle, and educational resources like in-app guidance and Help Center materials. These tools help users identify and contextualize synthetic content while promoting responsible use.
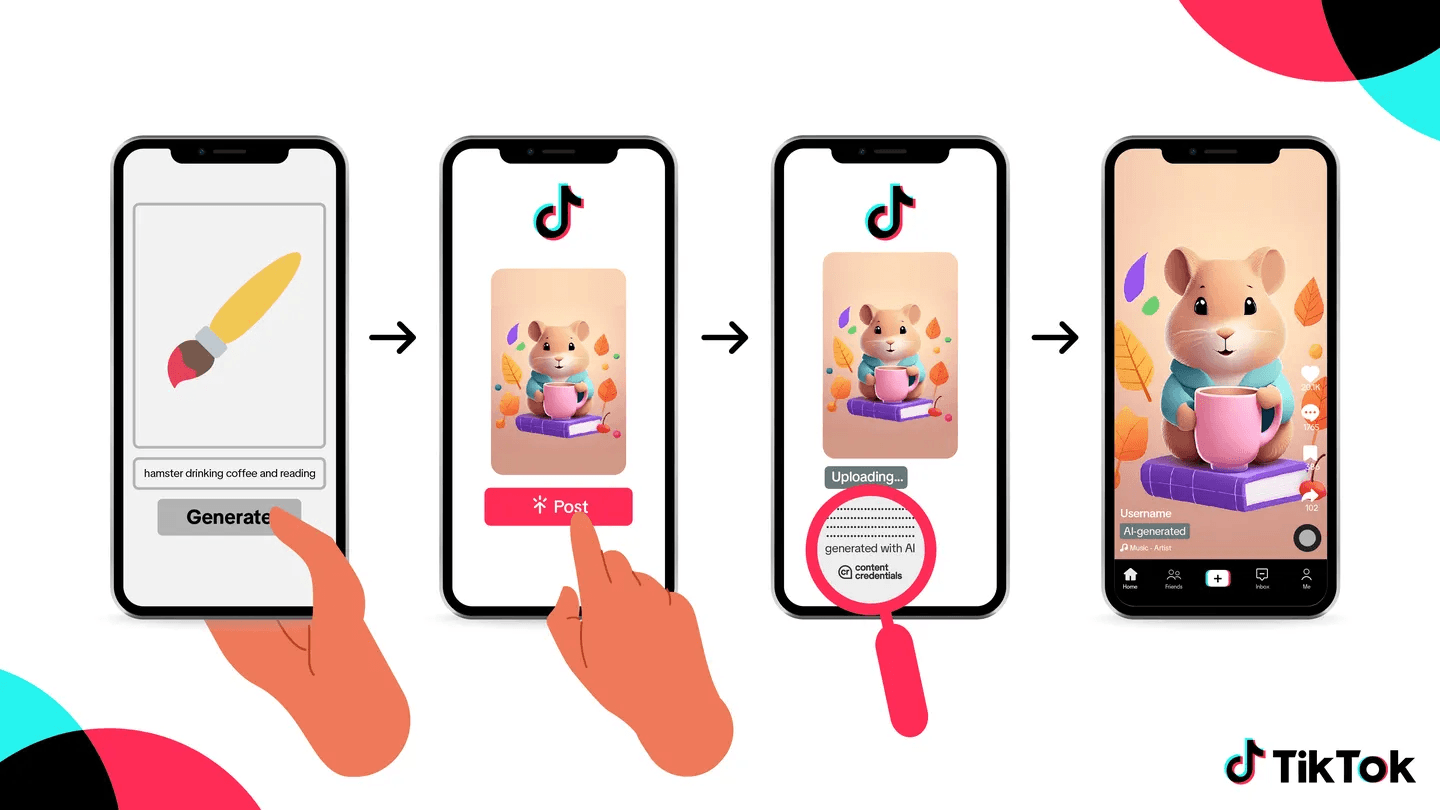
In May 2024, TikTok partnered with C2PA to implement Content Credentials, a metadata system that automatically labels AIGC by showing when and how it was created or edited. As the first video-sharing platform to adopt this technology, TikTok also joined Adobe’s Content Authenticity Initiative to encourage broader industry adoption.
TikTok continues to refine its policies and detection systems to combat harmful or misleading AIGC. A major challenge has been defining the scope of synthetic media while balancing its risks with creative potential. The platform supports watermarking, metadata, and content provenance from AI builders to enhance detection and labeling, advocating for industry collaboration to improve transparency and accountability in digital content.
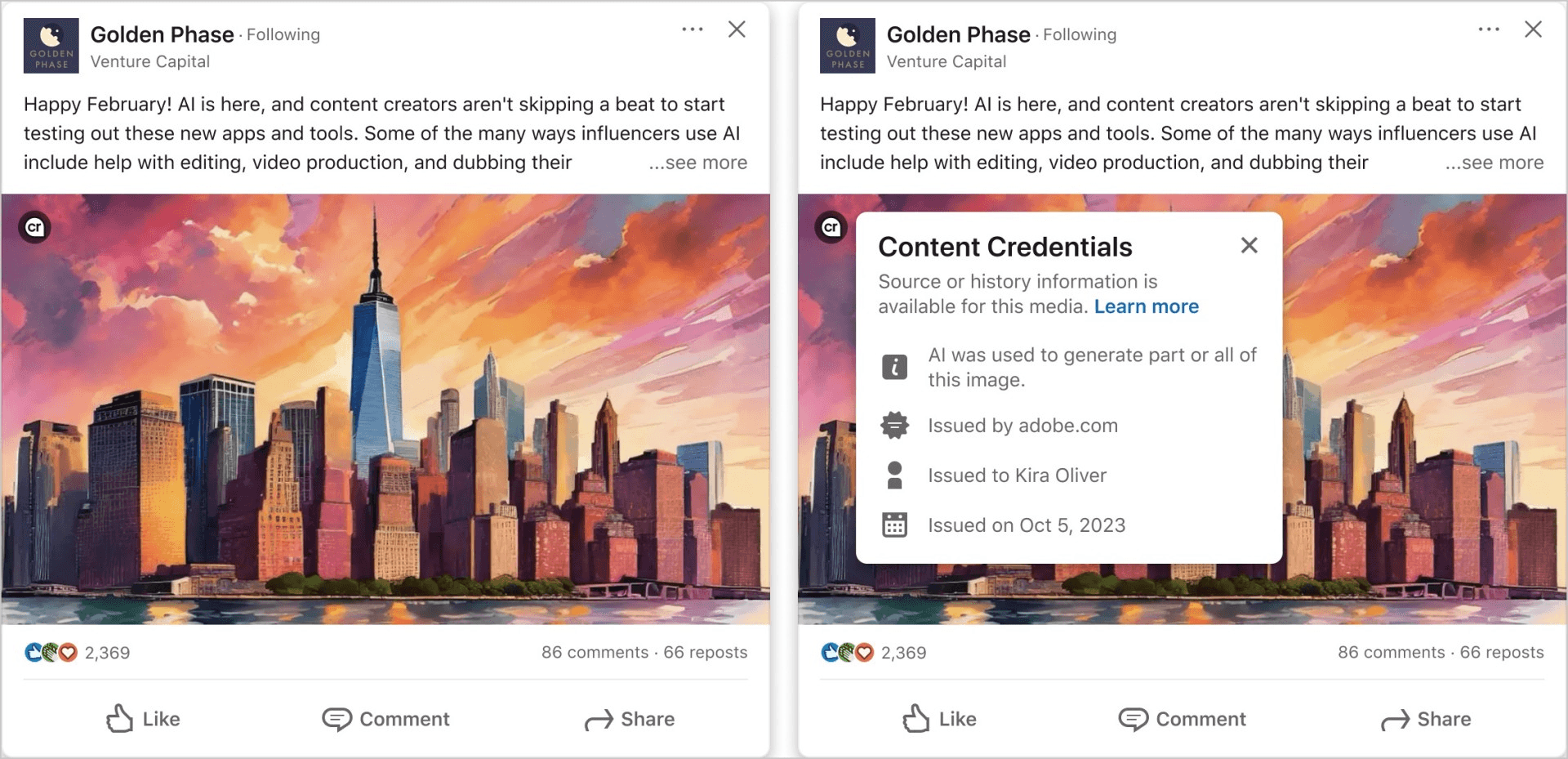
Starting in May 2024, LinkedIn began automatically labeling AI-generated content with C2PA Content Credentials. According to the Partnership on AI's "Synthetic Media Framework: Case Study," Content Credentials are displayed for all images and videos with cryptographically signed metadata uploaded to LinkedIn’s feed. Currently, LinkedIn acts as a display platform, showing existing C2PA Content Credentials but not generating new ones.
LinkedIn initially considered displaying detailed provenance information, including metadata about content creators and signers. However, to avoid risks from untrusted parties adding false claims, it now focuses on displaying only signer information—the entity that cryptographically signed the credentials—which it verifies against a trusted C2PA list. While LinkedIn ensures signer authenticity, it cannot verify the accuracy of all metadata claims.
The platform adheres to C2PA guidelines:
Level 1: Indicates whether C2PA data is present and validated.
Level 2: Summarizes the content's origin and changes.
These efforts contribute to addressing issues like fake profiles and help users identify whether images or videos in posts and articles were AI-generated.
However, LinkedIn’s success with content provenance relies on collaboration across the content pipeline, as well as better user knowledge. Tools like cameras, AI models (e.g., Adobe Firefly), and editing software (e.g., Photoshop) need to implement C2PA to embed Content Credentials. LinkedIn has also created an FAQ page to clarify Content Credentials and explain key terms, helping users navigate and understand provenance information more effectively.
Facebook, Instagram, Threads
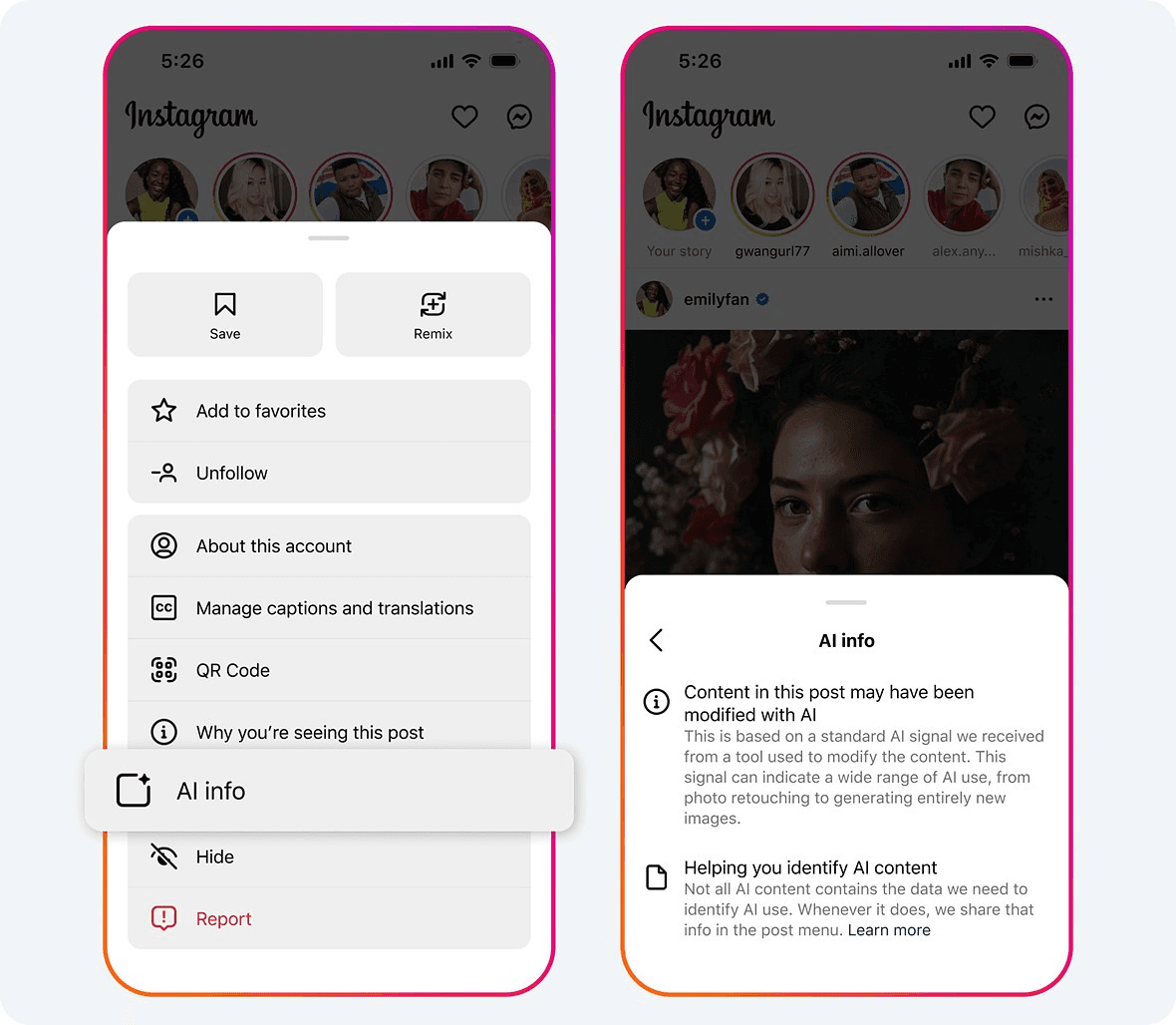
Starting in February 2024, Meta began implementing measures to ensure transparency around AI-generated and AI-edited content across its platforms, including Facebook, Instagram, and Threads.
According to the Partnership on AI's Case Study on Meta, the company embeds visible watermarks and labels for images created using Meta’s AI tools to indicate AI involvement. These images also include International Press Telecommunications Council (IPTC) metadata, which helps maintain transparency even when the content is shared outside Meta’s platforms. Additionally, Meta employs tools to detect invisible markers compliant with C2PA and IPTC standards to label AI-generated images from external sources.
Meta has also introduced a user disclosure feature that allows individuals to indicate if the content they post is AI-generated. This self-reporting mechanism supports transparency and ensures AI-generated content is properly labeled. Furthermore, Meta enforces policies requiring users to disclose photorealistic videos or realistic-sounding audio created or altered digitally. Non-compliance with these policies may result in penalties.
These initiatives reflect Meta’s commitment to responsible AI practices and a transparent user experience. By adopting C2PA and IPTC standards and joining the Coalition for C2PA in September, Meta has demonstrated its commitment to transparency and responsible AI practices.
Youtube
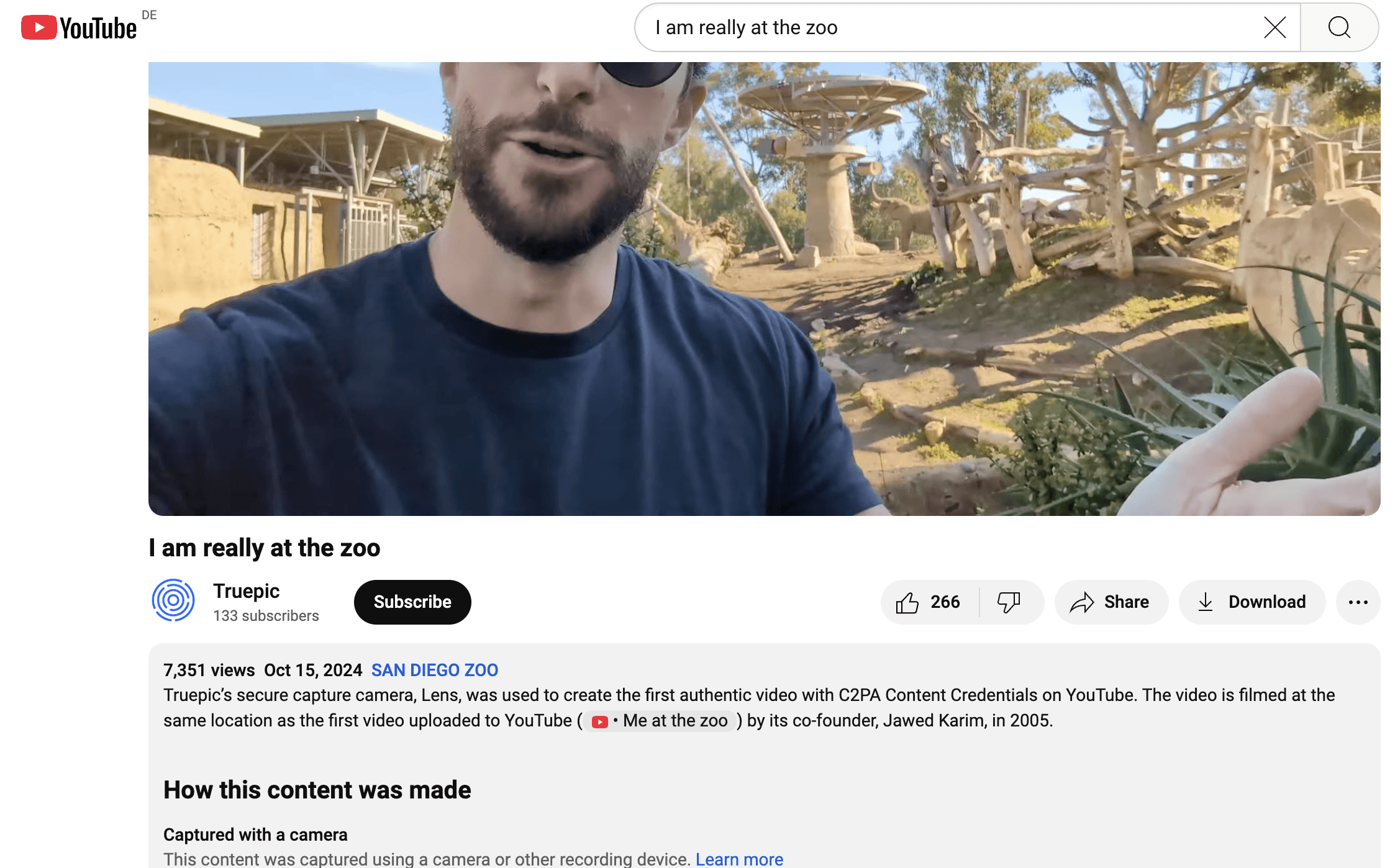
In October 2024, YouTube introduced a new feature indicating when a video was uploaded using a device compliant with C2PA standards, ensuring the content is authentic and unaltered from its original form. Google stated that this disclosure will appear on content captured using specific cameras, software, or mobile apps that meet C2PA standards.
SnapChat, X
In April 2024, Snapchat announced it would watermark AI-generated images created using its generative AI tools, adding a ghost logo with a sparkle icon to indicate the content was AI-generated. Unlike C2PA's standards, which embed metadata for verifying content authenticity and origin, Snapchat’s approach is focused on visual watermarks, without the metadata details. X also does not have an automatic labeling system and instead utilizes user-submitted "community notes" to identify and flag fake imagery.
Google Images & Google Ads
Google is actively integrating the Coalition for Content Provenance and Authenticity (C2PA) standards into its products to enhance transparency around digital content.
Google Images: Starting in October 2024, Google Images began displaying metadata for images in the "About this image" feature, providing users with detailed information when available. This feature offers insights, when available, on whether an image was AI-generated or edited, based on metadata provided by creators and publishers. The metadata is supplied by a signer, which could be a tool, device, or platform, such as a camera or image editing software, that adheres to the following requirements:
It implements C2PA version 2.1 or later.
The image’s manifest is certified by an authorized Certification Authority listed on the C2PA Trust List.
Google Ads: Google intends to extend C2PA metadata integration into its advertising systems. By embedding Content Credentials, Google aims to enforce key policies and ensure transparency in advertisements. This move is part of a broader effort to maintain trust and authenticity in digital advertising content.
These efforts show Google's dedication to embracing C2PA standards across its platforms, aiming to create a more transparent and trustworthy digital experience for its users.
Conclusion
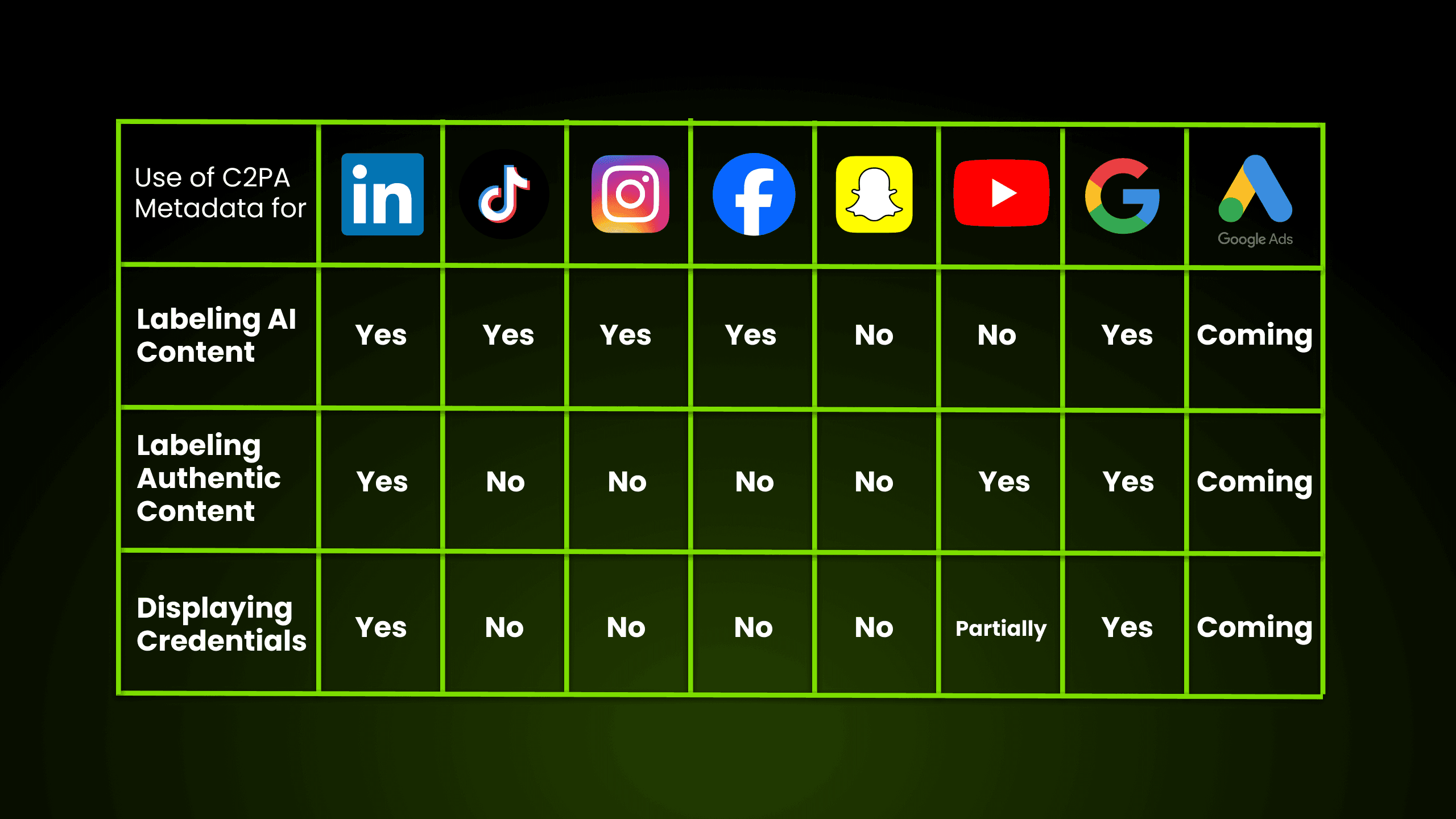
Here's a quick overview of the current state of C2PA integration across major social and advertising platforms:
As the digital landscape faces growing concerns over content authenticity, social media and advertising platforms are setting a strong precedent by adopting C2PA standards and similar transparency measures. These initiatives not only help combat misinformation but also address consumer demand for verifiable and trustworthy digital content. This showcases the importance of robust, standardized solutions like C2PA for ensuring transparency, building trust, and shaping the future of ethical content creation across social media.